Types of mortgage loans sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Mortgage loans are a fundamental aspect of the real estate market, playing a pivotal role in enabling individuals to purchase homes by spreading out payments over time. From fixed-rate to adjustable-rate mortgages, the landscape of mortgage options is vast and varied, providing borrowers with a range of choices to suit their financial needs.
Overview of Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are financial products that individuals use to purchase real estate properties. These loans allow borrowers to acquire a property by providing a down payment and then making regular payments over a period of time, typically 15 to 30 years.
Mortgage loans play a crucial role in the real estate market by enabling individuals to become homeowners without having to pay the full price of the property upfront. This accessibility to financing makes it possible for people to invest in their own homes and build equity over time.
Common Types of Mortgage Loans
- Conventional Loans: These are mortgage loans that are not insured or guaranteed by the government. Borrowers typically need good credit and a stable income to qualify for these loans.
- FHA Loans: Insured by the Federal Housing Administration, these loans are popular among first-time homebuyers due to their lower down payment requirements.
- VA Loans: These loans are guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs and are available to eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and certain military spouses.
- USDA Loans: Issued by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, these loans are designed to help individuals in rural areas purchase homes with no down payment.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages are a type of home loan where the interest rate remains the same for the entire duration of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will also remain constant throughout the life of the loan, providing predictability and stability in budgeting.
Comparison with Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages differ from adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) in that the interest rate on ARMs can fluctuate over time based on market conditions. While fixed-rate mortgages offer stability, ARMs may initially have lower interest rates but can increase significantly in the future.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Fixed-Rate Mortgages
One of the main benefits of fixed-rate mortgages is the predictability they offer, allowing borrowers to budget more effectively without the worry of rate increases. Additionally, fixed-rate mortgages protect borrowers from rising interest rates in the future.
However, a potential drawback of fixed-rate mortgages is that they typically have higher initial interest rates compared to ARMs. This means that borrowers may end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan, especially if they do not plan to stay in the home for a long period of time.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) are loans where the interest rate can change periodically, usually in relation to an index, such as the prime rate or Treasury bill rate. This means that your monthly mortgage payment can go up or down over time.
How Adjustable-Rate Mortgages Work
Adjustable-rate mortgages typically start with an initial fixed-rate period, after which the rate adjusts based on the index it is tied to. For example, a 5/1 ARM means the rate is fixed for the first 5 years and then adjusts annually. The adjustment period and caps on how much the rate can change are Artikeld in the loan terms.
Factors Affecting Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
- Economic conditions: Changes in the economy can impact the index rate, leading to adjustments in your ARM rate.
- Index fluctuations: Variations in the chosen index can directly affect your mortgage rate adjustments.
- Loan terms: The initial fixed-rate period, adjustment intervals, and rate caps all play a role in how your ARM functions.
Benefits of Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
- Lower initial rates: ARMs often offer lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages, making them attractive for buyers who plan to move or refinance before the rate adjusts.
- Potential for savings: If interest rates decrease or remain stable, borrowers with ARMs can benefit from lower monthly payments over time.
- Flexibility: For those who expect their income to increase in the future or plan to sell the property before the rate adjusts, ARMs provide flexibility in managing mortgage payments.
Government-Backed Mortgages
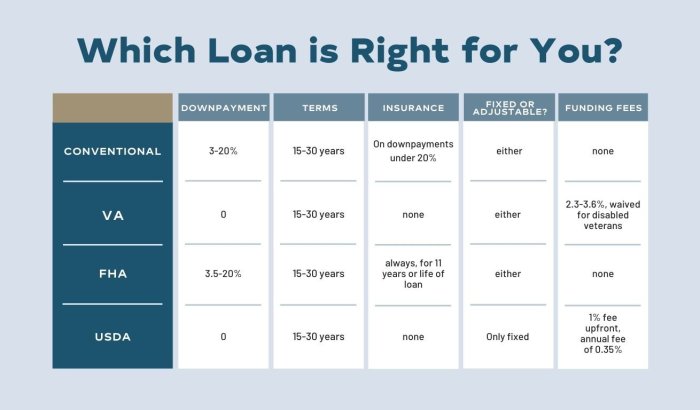
Government-backed mortgages are home loans that are guaranteed or insured by the government. These types of loans help make homeownership more accessible to individuals who may not qualify for conventional mortgages. Some common government-backed mortgage programs include FHA (Federal Housing Administration), VA (Department of Veterans Affairs), and USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) loans.
FHA Loans
FHA loans are popular among first-time homebuyers and those with less-than-perfect credit. They require a lower down payment compared to conventional loans and have more flexible qualification requirements. Borrowers must pay mortgage insurance premiums for the life of the loan.
VA Loans
VA loans are available to eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and certain spouses. These loans offer competitive interest rates, no down payment requirement, and no private mortgage insurance. VA loans are guaranteed by the VA, making them a low-risk option for lenders.
USDA Loans
USDA loans are designed to help low to moderate-income borrowers in rural areas achieve homeownership. These loans offer 100% financing, low-interest rates, and reduced mortgage insurance costs. Borrowers must meet income eligibility requirements and the property must be located in a designated rural area.
Overall, government-backed mortgages provide borrowers with more flexible terms and lower down payment options compared to conventional loans. Each program has specific eligibility criteria, so it’s important for borrowers to research and understand the requirements before applying.
Jumbo Loans
Jumbo loans are mortgages that exceed the conforming loan limits set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA). These loans are typically used to finance higher-priced properties that exceed the limits for conventional loans.
Differences between Jumbo Loans and Conventional Loans
- Jumbo loans have higher loan amounts than conventional loans, making them ideal for luxury properties or high-cost areas.
- Interest rates for jumbo loans are usually higher than those for conventional loans due to the increased risk for lenders.
- Down payment requirements for jumbo loans are typically higher than those for conventional loans, often ranging from 10% to 20%.
- Qualifying for a jumbo loan may require a higher credit score and lower debt-to-income ratio compared to conventional loans.
Requirements for Obtaining a Jumbo Loan
- Borrowers seeking a jumbo loan will need to provide proof of income, assets, and employment to demonstrate their ability to repay the loan.
- A strong credit score is essential for obtaining a jumbo loan, with most lenders requiring a score of 700 or higher.
- Debt-to-income ratio is closely scrutinized for jumbo loans, with lenders typically looking for a ratio of 43% or lower.
- Appraisals for jumbo loans are more detailed and may require additional documentation to justify the higher loan amount.
Interest-Only Mortgages
Interest-only mortgages are a type of loan where the borrower is only required to pay the interest on the loan for a certain period, typically the first 5 to 10 years of the loan term. This means that the monthly payments are lower during this initial period compared to a traditional mortgage where payments include both interest and principal.
How Interest-Only Mortgages Work
Interest-only mortgages work by allowing borrowers to make lower monthly payments during the initial period of the loan term. This can be beneficial for borrowers who expect their income to increase in the future or those who plan to sell the property before the principal payments kick in. However, once the interest-only period ends, borrowers will have to start making payments towards both the principal and interest, which can lead to higher monthly payments.
Pros and Cons of Interest-Only Mortgages
- Pros:
- Lower initial monthly payments make it easier for borrowers to qualify for a larger loan amount.
- Flexibility for borrowers who expect a significant increase in income or plan to sell the property before the principal payments start.
- Can be a good option for real estate investors looking to maximize cash flow.
- Cons:
- Higher risk of payment shock once the interest-only period ends and principal payments begin.
- May end up paying more interest over the life of the loan compared to a traditional mortgage.
- Property values may not increase as expected, leaving borrowers in a difficult financial situation.