As How to file taxes takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with american high school hip style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Navigating the world of taxes can be confusing, but fear not – this guide will break it down in a way that’s easy to understand and apply to your own situation.
Understanding Taxes
When it comes to taxes, it’s all about contributing a portion of your income to the government. This money is used to fund public services like schools, roads, and healthcare. It’s a way of ensuring that everyone contributes their fair share to society.
Types of Taxes
There are several types of taxes that individuals may need to file:
- Income Tax: This is a tax on the money you earn from working, investments, or other sources.
- Property Tax: This tax is based on the value of your real estate or personal property.
- Sales Tax: A tax added to the price of goods and services at the point of sale.
- Capital Gains Tax: This tax is applied to the profits made from selling assets like stocks or real estate.
Importance of Filing Taxes
Filing your taxes accurately and on time is crucial for several reasons:
- Compliance: Filing taxes is a legal requirement, and failing to do so can result in penalties or fines.
- Refunds: By filing your taxes, you may be eligible for tax refunds if you’ve overpaid throughout the year.
- Credit Score: Filing taxes can also impact your credit score, as it shows financial responsibility and stability.
Required Documents
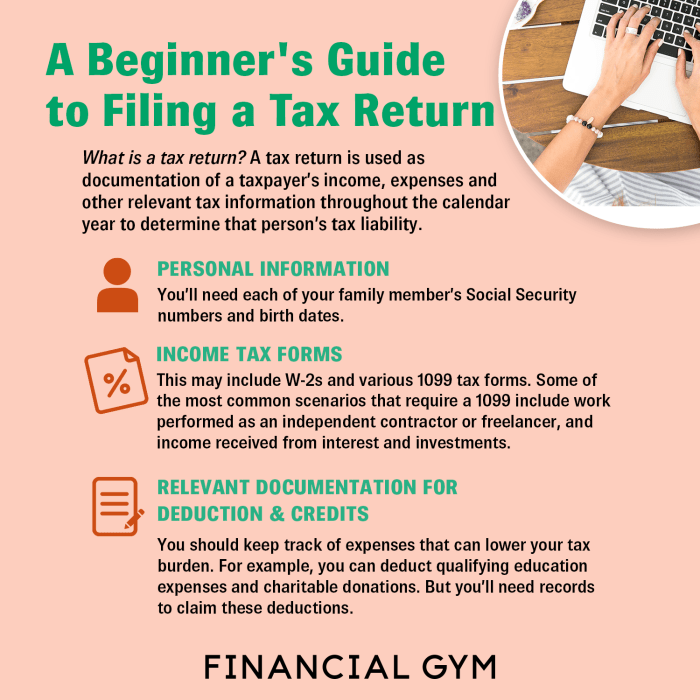
To file your taxes accurately and efficiently, you’ll need to gather certain essential documents. These documents provide important information about your income, deductions, and credits, helping you complete your tax return correctly.
W-2 Forms
- W-2 forms are crucial for employees as they show the wages earned and taxes withheld from your paycheck throughout the year.
- You can obtain your W-2 from your employer by the end of January each year.
1099 Forms
- 1099 forms are necessary if you received income as an independent contractor, freelancer, or from investments.
- If you’re missing a 1099 form, reach out to the issuer directly to request a copy.
Other Important Documents
- Receipts for charitable donations, medical expenses, and business expenses, if applicable.
- Mortgage interest statements, property tax records, and student loan interest statements.
- Social Security numbers for yourself, your spouse, and dependents.
Tips for Organization
- Keep all tax-related documents in one designated folder or digital folder throughout the year.
- Label folders or files with tax year to easily differentiate and locate documents when needed.
- Consider using a cloud storage service for digital copies of important documents for safekeeping.
Filing Options
When it comes to filing your taxes, you have several options to choose from. Each method has its own set of pros and cons, so it’s important to understand the differences before deciding which one is right for you.
Online Software
- Pros:
- Convenient and easy to use.
- May offer step-by-step guidance.
- Can help maximize deductions and credits.
- Cons:
- May not be suitable for complex tax situations.
- Costs associated with using the software.
- Potential security risks with online data.
Hiring a Professional
- Pros:
- Expertise and knowledge of tax laws.
- Can provide personalized advice.
- May help avoid errors and audits.
- Cons:
- Can be expensive.
- Dependent on the availability of the professional.
- Less control over the process.
Paper Filing
- Pros:
- May be preferred for those who are not tech-savvy.
- No cost associated with filing on paper.
- Can be a more tangible record of your taxes.
- Cons:
- Higher chance of errors and mistakes.
- Processing time may be longer.
- Limited access to help and guidance.
Deductions and Credits
When it comes to filing taxes, understanding the difference between tax deductions and tax credits is crucial. Tax deductions reduce the amount of income that is subject to taxation, while tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed.
Tax Deductions
Tax deductions lower your taxable income, which in turn can reduce the amount of tax you owe. Some common deductions include:
- Mortgage interest
- Charitable contributions
- Medical expenses
- State and local taxes
Tax Credits
Tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the actual amount of tax owed. Here are some examples of tax credits:
- Child Tax Credit
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education credits
- Retirement savings contributions credit
Reducing Tax Liabilities
By taking advantage of deductions and credits, individuals can significantly reduce their tax liabilities. For example, if you have a tax liability of $2,000 but qualify for a $500 tax credit, your tax liability would be reduced to $1,500. Similarly, if you have $50,000 in taxable income but can deduct $10,000 in mortgage interest, your taxable income would be reduced to $40,000.
Filing Process
When it comes to filing your taxes, it’s important to follow a step-by-step process to ensure accuracy and avoid any potential pitfalls. By understanding the filing process and being aware of common mistakes, you can make sure your tax filing experience goes smoothly and efficiently.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2s, 1099s, receipts, and any other relevant paperwork.
- Choose the best filing option for your situation, whether it’s online, through tax software, or with the help of a professional.
- Fill out your tax forms carefully, double-checking all information for accuracy.
- Submit your completed tax return by the deadline, either electronically or by mail.
Avoiding Pitfalls
- Avoid rushing through the process, take your time to ensure all information is correct.
- Double-check all calculations to prevent errors that could lead to penalties or delays.
- Be cautious of tax scams and phishing attempts, only provide personal information to trusted sources.
Tips for a Smooth Filing Experience
- Keep organized records throughout the year to make tax time easier.
- Consider filing early to avoid the last-minute rush and potential mistakes.
- If you’re unsure about any part of the process, seek help from a tax professional or use reputable tax software.