Buckle up, folks! Today we’re diving into the world of fixed vs variable loan rates, where the game is all about making the right financial moves. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of loan rates, from the stable ground of fixed rates to the unpredictable territory of variable rates. It’s time to level up your financial knowledge and make informed decisions like a pro.
Fixed vs Variable Loan Rates
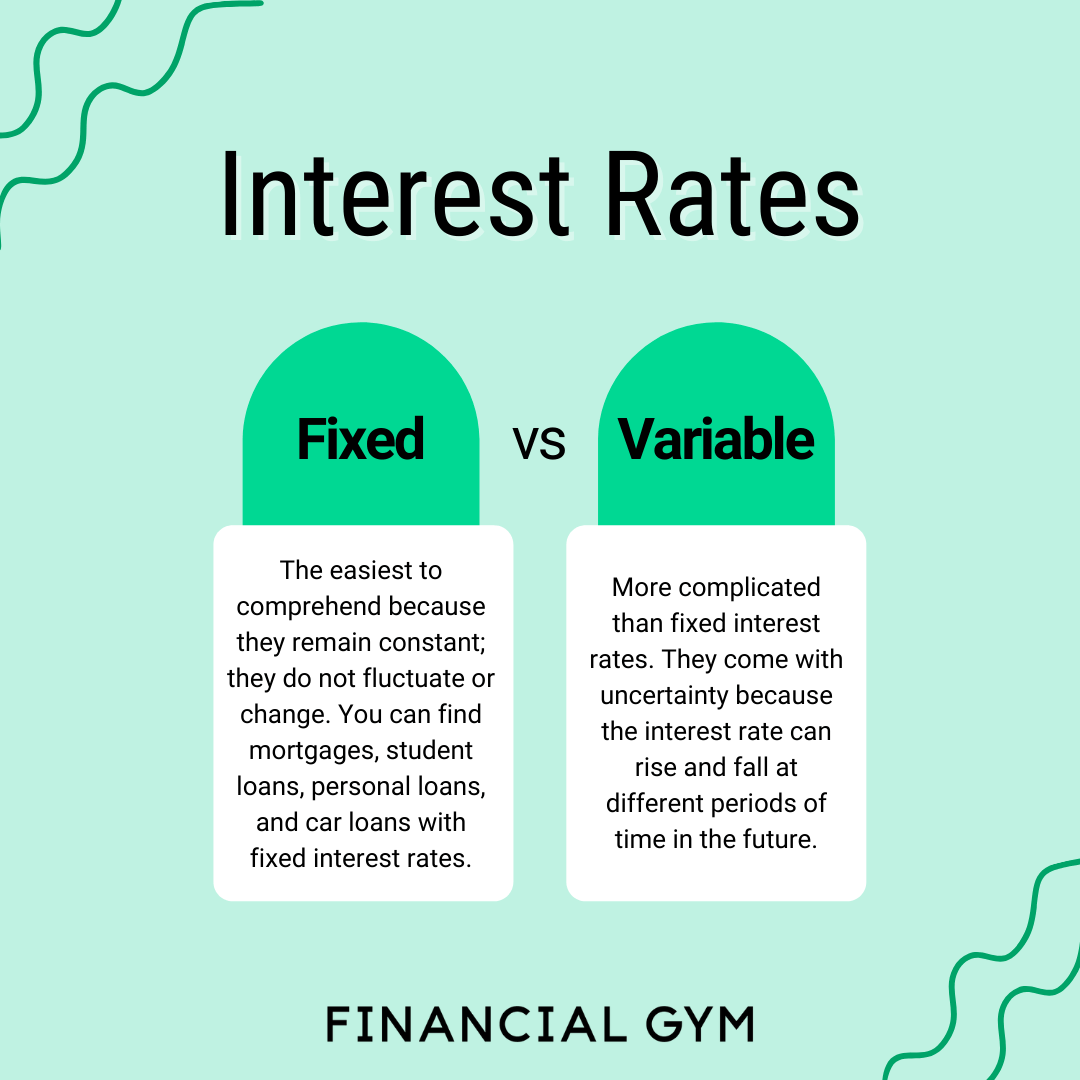
When it comes to loan rates, borrowers have the option to choose between fixed and variable interest rates. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered before making a decision.
Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that the monthly payment amount will not change, providing predictability and stability for borrowers. It is ideal for individuals who prefer to have a consistent budget without worrying about fluctuating rates.
- Advantages of Fixed Rate Loans:
- Protection against rising interest rates
- Predictable monthly payments
- Easier budgeting and planning
- Disadvantages of Fixed Rate Loans:
- Initial interest rates might be higher than variable rates
- Borrowers may miss out on savings if market rates decrease
- Less flexibility compared to variable rates
Variable Interest Rates
Variable interest rates, on the other hand, can fluctuate based on market conditions. These rates are usually tied to an index, such as the prime rate, and can change periodically, resulting in varying monthly payments for borrowers. While initial rates may be lower than fixed rates, there is a level of uncertainty involved.
- Advantages of Variable Rate Loans:
- Potential for lower initial interest rates
- Opportunity to benefit from rate decreases
- Flexibility in terms of prepayment options
- Disadvantages of Variable Rate Loans:
- Risk of rates increasing over time
- Unpredictable monthly payments
- Challenges in long-term budgeting
Factors Influencing Loan Rate Type Selection
When choosing between fixed and variable loan rates, borrowers need to consider several key factors to make an informed decision. These factors can impact their overall financial stability and the cost of borrowing money. Let’s explore some of the most important considerations below.
Economic Conditions Impact
Economic conditions play a crucial role in determining whether a fixed or variable rate loan is more suitable for a borrower. In a stable or rising interest rate environment, opting for a fixed rate can provide certainty and protect against potential rate hikes in the future. On the other hand, in a declining interest rate environment, a variable rate loan may offer lower initial rates and potential savings over time.
Examples of Beneficial Scenarios
1. Homebuyers who plan to stay in their property for an extended period may benefit from a fixed rate mortgage as it provides predictability in monthly payments and protects against interest rate fluctuations.
2. Business owners seeking a short-term loan for a specific project may opt for a variable rate loan to take advantage of lower initial rates and potentially save on interest costs if rates remain low.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
When it comes to choosing between fixed and variable loan rates, understanding the risks involved is crucial. Let’s dive into how each type can impact borrowers and strategies to mitigate these risks.
Stability with Fixed Rates
Fixed rates provide stability in monthly payments because the interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term. This means borrowers can budget effectively without worrying about fluctuations in their payments.
Managing Risks with Variable Rates
Variable rates, on the other hand, come with the risk of interest rate fluctuations. These fluctuations can lead to unpredictable changes in monthly payments, making it challenging for borrowers to plan their finances effectively.
One way borrowers can mitigate these risks is by closely monitoring the market trends and economic indicators that influence interest rates. By staying informed, borrowers can anticipate potential changes and be prepared to adjust their budgets accordingly.
Another strategy is to consider a hybrid loan option that combines elements of both fixed and variable rates. This provides a middle ground for borrowers who want some stability in their payments while still being able to benefit from potential interest rate decreases.
Effective Interest Rate Management Strategies
For borrowers with variable rates, it’s essential to have a contingency plan in place to deal with sudden increases in interest rates. This could include setting aside a buffer fund or exploring refinancing options to lock in a lower rate when the market conditions are favorable.
Additionally, borrowers can consider making extra payments towards their principal balance when interest rates are low. This can help reduce the overall interest costs and shorten the loan term, providing some protection against future rate hikes.
Market Trends and Predictions
In the realm of fixed and variable loan rates, market trends play a significant role in determining the direction of interest rates. Analyzing historical patterns can provide valuable insights into how these rates have behaved over time.
When examining historical trends, it is evident that fixed rates tend to remain stable over extended periods, offering borrowers a sense of security in knowing their interest payments won’t fluctuate. On the other hand, variable rates have shown to be more reactive to market conditions, rising and falling based on factors such as economic indicators and central bank decisions.
Market conditions, such as inflation rates, economic growth, and government policies, heavily influence the movement of fixed and variable loan rates. For example, during times of economic uncertainty, central banks may opt to lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending, resulting in lower variable rates. Conversely, in times of economic prosperity, interest rates may rise, impacting both fixed and variable rates.
Looking ahead, predictions for future trends in fixed and variable loan rates are subject to a variety of factors. Economic forecasts, employment data, and inflation expectations all play a role in shaping interest rate movements. Additionally, geopolitical events and global economic conditions can also impact interest rates, influencing the decision-making process for borrowers choosing between fixed and variable rates.
Predicted Future Trends
- Experts predict that fixed rates may see a gradual increase in the coming years as economic growth continues and inflation picks up.
- Variable rates are expected to remain relatively low in the short term, but could see an uptick if central banks decide to tighten monetary policy.
- Global economic uncertainties, such as trade tensions and geopolitical risks, could introduce volatility into interest rates, making it crucial for borrowers to stay informed and adaptable.