Credit history report sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with American high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we dive deeper into the components and factors affecting credit history reports, you’ll uncover the key insights needed to navigate the financial landscape with finesse.
Importance of Credit History Report
A credit history report is a crucial tool for making informed financial decisions. It provides a detailed record of an individual’s credit activity and payment history, which is used by lenders to assess creditworthiness.
Lenders’ Evaluation of Credit Reports
Lenders use credit reports to determine the level of risk associated with lending money to an individual. They analyze factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, and types of credit accounts.
Having a good credit history report can increase the likelihood of approval for loans and credit cards, as it demonstrates responsible financial behavior.
Benefits of a Good Credit History Report
- Access to better interest rates: A high credit score resulting from a good credit history report can lead to lower interest rates on loans and credit cards.
- Higher credit limits: Lenders are more likely to offer higher credit limits to individuals with a positive credit history, allowing for greater purchasing power.
- Approval for rental applications: Landlords often review credit reports to assess a tenant’s financial responsibility, making a good credit history report important for securing rental accommodations.
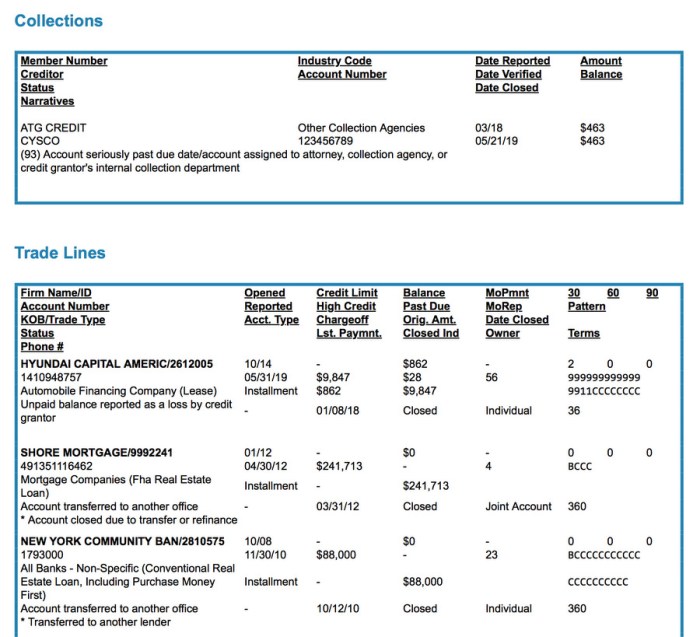
Components of a Credit History Report
When we talk about a credit history report, there are several key components that make up this important document. Each section provides valuable information about your financial background and creditworthiness, helping lenders make informed decisions when considering your applications for credit.
Personal Information
The personal information section of a credit history report includes details such as your name, address, date of birth, and Social Security number. This information is crucial for identifying you and ensuring that the credit report belongs to the correct individual.
Account History
Your account history is a vital part of your credit history report as it shows a detailed record of your credit accounts, including credit cards, loans, and mortgages. This section typically includes information on your payment history, account balances, credit limits, and any late or missed payments. Lenders use this data to assess your credit management skills and payment behavior.
Inquiries
The inquiries section of a credit history report lists all the times your credit report has been accessed by lenders or other authorized parties. There are two types of inquiries – hard inquiries, which occur when you apply for credit, and soft inquiries, which happen when a lender pre-approves you for a credit offer. Hard inquiries can impact your credit score, so it’s essential to monitor them carefully.
Public Records
Public records on a credit history report include information such as bankruptcies, foreclosures, tax liens, and civil judgments. These negative marks can significantly impact your credit score and overall creditworthiness. Lenders use this information to evaluate your financial stability and risk level when considering your credit applications.
Updating and Maintaining Information
Information on a credit history report is regularly updated by creditors and credit bureaus. Lenders report your account activity, payment history, and balances to the credit bureaus, who then update your credit report accordingly. It’s essential to review your credit report regularly to ensure that all information is accurate and up-to-date. If you spot any errors, you can dispute them with the credit bureau to have them corrected.
Factors Affecting Credit History
When it comes to credit history, there are several key factors that can greatly impact an individual’s credit report. These factors play a significant role in determining a person’s credit score and overall creditworthiness.
Payment History
Maintaining a good payment history is crucial for a positive credit report. Late payments, defaults, or bankruptcies can significantly lower a credit score. It is essential to pay bills on time and in full to show responsible financial behavior.
Credit Utilization
Credit utilization refers to the amount of credit being used compared to the total credit available. High credit utilization can indicate financial strain and may negatively affect a credit score. It is recommended to keep credit utilization below 30% to demonstrate responsible credit management.
Length of Credit History
The length of credit history is another important factor in determining creditworthiness. A longer credit history provides lenders with more information about a person’s financial habits. It is advisable to keep old accounts open to maintain a longer credit history.
Types of Credit
Having a diverse mix of credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can positively impact a credit score. Lenders like to see that individuals can manage different types of credit responsibly. It is beneficial to have a healthy mix of credit accounts.
Tips to Maintain or Improve Credit History
1. Pay bills on time and in full to establish a positive payment history.
2. Keep credit utilization low by not maxing out credit cards.
3. Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts in a short period.
4. Monitor credit reports regularly for errors and fraudulent activity.
5. Consider using credit responsibly to build a strong credit history over time.
Obtaining and Reviewing a Credit History Report
When it comes to obtaining and reviewing a credit history report, it’s essential to know how to navigate the process effectively. Understanding how to obtain a free credit report from major credit bureaus, interpret the information presented, and take action in case of errors is crucial for managing your financial health.
Obtaining a Free Credit Report
- Visit AnnualCreditReport.com, the only authorized website for free credit reports under federal law.
- Choose which credit bureau report you want to view: Equifax, Experian, or TransUnion.
- Provide your personal information, including name, address, Social Security number, and date of birth.
- Verify your identity through a series of security questions.
- Review and download your credit report from each bureau for free once every 12 months.
Interpreting and Reviewing a Credit History Report
- Check for accuracy in personal information, account details, payment history, and credit inquiries.
- Look for any unfamiliar accounts, late payments, collections, or errors that could impact your credit score.
- Understand the different sections of the report, including open accounts, closed accounts, and public records.
- Review your credit score and understand how it is calculated based on the information in the report.
Addressing Errors or Discrepancies
- If you find errors in your credit report, file a dispute with the credit bureau reporting the inaccurate information.
- Provide supporting documents or evidence to substantiate your claim of errors or discrepancies.
- Follow up with the credit bureau to ensure the corrections are made and reflected in your updated credit report.
- Monitor your credit report regularly to ensure the accuracy of the information presented and take action promptly if new errors arise.