Diving into the realm of variable interest rate loans opens up a dynamic landscape of financial opportunities and risks. As we navigate through the intricacies of this topic, we uncover the nuances that make variable interest rate loans both intriguing and complex.
Exploring the realm of interest rates, we uncover the ever-changing nature of variable interest rate loans and the impact they have on borrowers and financial institutions alike.
Introduction to Variable Interest Rate Loans
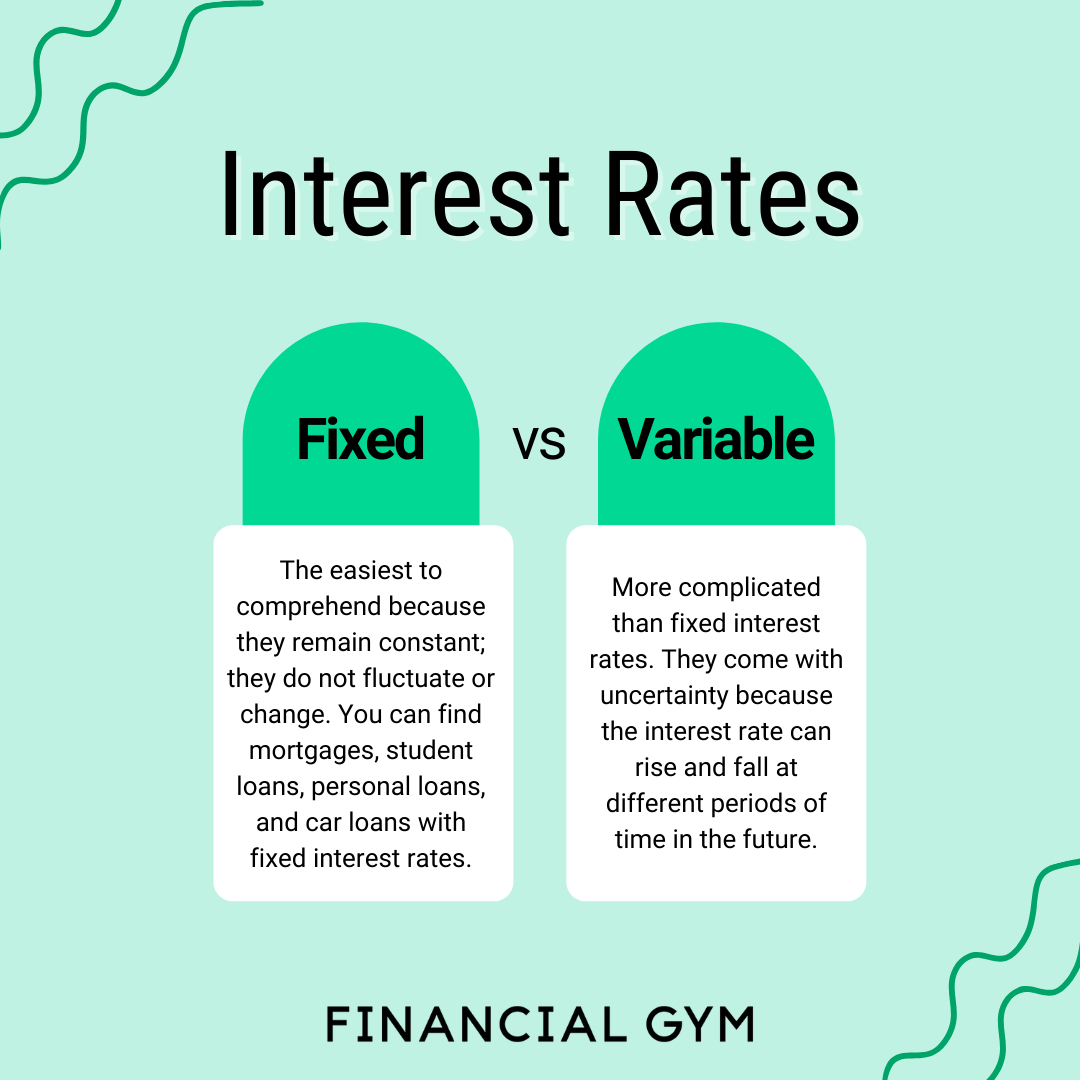
Variable interest rate loans are loans where the interest rate can change over time based on fluctuations in the market. This means that your monthly payments can go up or down depending on the movement of interest rates.
Some financial institutions that offer variable interest rate loans include banks like Wells Fargo, Chase, and Bank of America, as well as credit unions and online lenders.
Variable interest rates differ from fixed interest rates in that fixed rates stay the same for the entire term of the loan, providing predictability in monthly payments. On the other hand, variable rates can offer lower initial rates but come with the risk of increasing rates in the future.
Factors Influencing Variable Interest Rates
Variable interest rates are influenced by a variety of economic factors, market conditions, and central bank policies. These factors can cause fluctuations in interest rates, impacting borrowers and lenders alike.
Economic Factors Impacting Variable Interest Rates
- Supply and Demand: When there is high demand for credit, interest rates tend to rise. Conversely, when demand is low, interest rates may fall.
- Inflation Rates: Higher inflation rates typically lead to higher interest rates as lenders seek to protect their returns from the eroding effects of inflation.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can push interest rates higher as borrowers are willing to pay more for credit in a booming economy.
Market Conditions and Variable Interest Rates
- Global Events: Uncertainty in global markets can impact interest rates, causing them to rise or fall based on market sentiment and investor confidence.
- Government Bond Yields: Changes in government bond yields can influence variable interest rates, as these rates are often used as benchmarks for lending rates.
- Banking Competition: Increased competition among banks can lead to lower interest rates as lenders vie for customers by offering more attractive loan terms.
Role of Central Banks in Influencing Variable Interest Rates
- Monetary Policy: Central banks use tools like setting the benchmark interest rate to influence lending rates throughout the economy.
- Open Market Operations: Central banks can buy or sell government securities to adjust the money supply, impacting interest rates in the broader financial market.
- Regulation and Oversight: Central banks play a crucial role in regulating the banking sector, ensuring stability and sound lending practices that can impact variable interest rates.
Pros and Cons of Variable Interest Rate Loans
When considering a variable interest rate loan, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages to make an informed decision.
Advantages of Choosing a Variable Interest Rate Loan
- Lower initial interest rates: Variable interest rate loans often start with lower rates compared to fixed-rate loans, allowing borrowers to save money in the beginning.
- Potential for lower rates in the future: If market interest rates decrease, borrowers with variable rate loans can benefit from reduced monthly payments.
- Flexibility: Variable rate loans typically offer more flexibility in terms of repayment options and early pay-off without penalty.
Risks Associated with Variable Interest Rate Loans
- Uncertainty: The main risk of variable rate loans is the uncertainty of future interest rate fluctuations, which can lead to higher monthly payments.
- Financial strain: If interest rates rise significantly, borrowers may face challenges in managing increased loan payments, potentially impacting their financial stability.
- Interest rate caps: Some variable rate loans have caps on how much the interest rate can increase, but these caps may still result in higher payments than initially planned.
Comparison with Fixed-Rate Loans in Terms of Flexibility
- Fixed-rate loans offer stable monthly payments throughout the loan term, providing predictability for budgeting purposes.
- Variable rate loans, on the other hand, can be advantageous for borrowers who expect interest rates to decrease in the future or plan to pay off the loan sooner with the flexibility to benefit from lower rates.
- Overall, choosing between variable and fixed-rate loans depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and market expectations.
Managing Variable Interest Rate Loans
Managing variable interest rate loans can be challenging due to the uncertainty of fluctuating rates. It is essential for borrowers to have strategies in place to navigate these changes effectively.
Monitoring Interest Rate Trends
Keeping a close eye on interest rate trends is crucial for borrowers with variable rate loans. By monitoring these trends, borrowers can anticipate potential changes in their loan payments and make informed decisions regarding their finances.
- Regularly check financial news sources and websites for updates on interest rates.
- Stay informed about economic indicators that may influence interest rate movements, such as inflation rates and Federal Reserve decisions.
- Consider setting up alerts or notifications to stay updated on any significant changes in interest rates.
Refinancing as a Management Tool
Refinancing can be a powerful tool for managing variable interest rate loans. By refinancing, borrowers can potentially secure a lower fixed interest rate or switch to a more stable loan structure to avoid future rate fluctuations.
- Compare current interest rates with the rate on your existing loan to determine if refinancing could lead to cost savings.
- Consult with financial advisors or loan experts to explore refinancing options and understand the potential benefits and drawbacks.
- Be mindful of any associated costs or fees with refinancing and calculate whether the long-term savings outweigh the upfront expenses.