Hey there! Ready to dive into some tax planning tips that will help you keep more of your hard-earned money? Buckle up as we explore the ins and outs of tax planning with a fresh perspective and practical insights that you can start using today.
In this guide, we’ll uncover the importance of tax planning, different strategies to minimize your tax liability, maximizing deductions and credits, retirement planning tips, and smart ways to plan your investments for tax efficiency. Let’s get started!
Importance of Tax Planning
Tax planning is like the secret sauce for your financial recipe, whether you’re an individual or running a business. It’s all about strategizing to minimize the amount of taxes you owe while staying within the boundaries of the law.
Key Benefits of Effective Tax Planning
- Maximizing tax deductions: By planning ahead and taking advantage of available deductions, you can reduce your taxable income and ultimately pay less in taxes.
- Lowering tax liability: With effective tax planning, you can find legal ways to reduce the amount of taxes you owe, leaving more money in your pocket.
- Improving cash flow: By managing your taxes efficiently, you can free up cash that can be reinvested in your business or used for personal financial goals.
Examples of How Tax Planning Can Help Save Money
-
Utilizing retirement accounts: Contributing to retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA not only helps you save for the future but also provides tax benefits by reducing your taxable income.
- Timing capital gains: Selling investments strategically can help you minimize capital gains taxes by taking advantage of lower tax rates or offsetting gains with losses.
- Optimizing business expenses: Properly tracking and deducting business expenses can lower your taxable income and save you money on taxes.
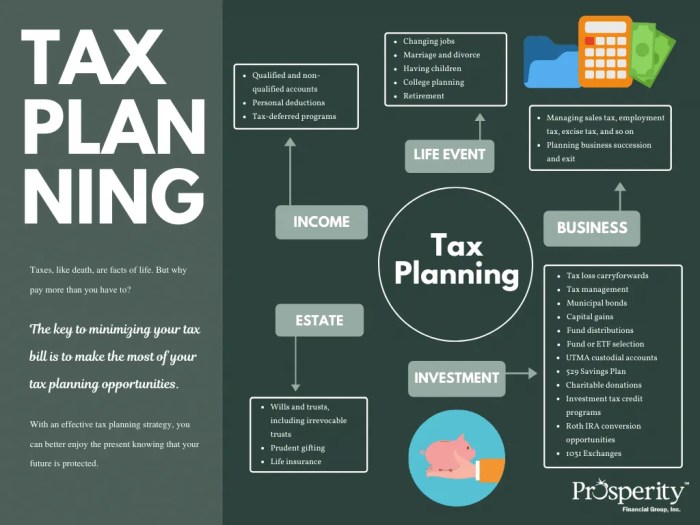
Strategies for Tax Planning
Tax planning is essential for minimizing tax liability and maximizing financial efficiency. By utilizing various strategies, individuals and businesses can optimize their tax situations and save money in the long run.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Strategies
When it comes to tax planning, it is crucial to consider both short-term and long-term strategies. Short-term strategies focus on immediate tax savings, such as deductions and credits for the current tax year. On the other hand, long-term strategies involve planning for future tax obligations and structuring investments to reduce tax liability over time.
- Short-Term Strategies:
- Maximizing deductions such as charitable contributions and business expenses.
- Taking advantage of tax credits for education, energy-efficient home improvements, or childcare expenses.
- Deferring income to the following year to reduce taxable income for the current year.
- Long-Term Strategies:
- Investing in tax-efficient accounts like Roth IRAs or 401(k)s to minimize taxes on investment gains.
- Utilizing estate planning techniques to minimize estate taxes for future generations.
- Implementing a tax-loss harvesting strategy to offset capital gains with capital losses.
Year-Round Tax Planning Methods
Tax planning should not be a once-a-year activity. By implementing strategies throughout the year, individuals and businesses can stay ahead of their tax obligations and make informed financial decisions.
- Regularly review and update your financial goals and tax situation to identify potential tax-saving opportunities.
- Monitor changes in tax laws and regulations to adapt your tax planning strategies accordingly.
- Utilize tax-efficient investment strategies to minimize taxes on investment income and capital gains.
- Consider tax implications before making major financial decisions such as buying a home, starting a business, or selling investments.
Tax Deductions and Credits
When it comes to taxes, understanding the difference between tax deductions and tax credits is crucial for maximizing your savings. Tax deductions reduce your taxable income, while tax credits directly reduce the amount of taxes you owe.
Common Tax Deductions
- Home mortgage interest
- Charitable donations
- State and local taxes
- Medical expenses
- Educational expenses
Tax Credits for Individuals and Businesses
- The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) for low to moderate-income individuals
- The Child Tax Credit for families with dependent children
- The Lifetime Learning Credit for educational expenses
- The Research and Development Credit for businesses investing in research and development
Retirement Planning and Taxes
When it comes to retirement planning, it’s essential to consider the impact it can have on your tax obligations. The decisions you make now can significantly affect how much you owe in taxes during your retirement years.
Tax Implications of Different Retirement Accounts
- 401(k): Contributions made to a traditional 401(k) are typically tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income in the year you make the contribution. However, withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- IRA: Similar to a 401(k), contributions to a traditional IRA are tax-deductible, but withdrawals are taxed as income. Roth IRAs, on the other hand, are funded with after-tax dollars, so withdrawals in retirement are typically tax-free.
Optimizing Retirement Savings to Minimize Taxes
- Consider a mix of retirement accounts: Diversifying your retirement savings across different account types can provide flexibility in retirement and help manage tax implications.
- Take advantage of tax-efficient investment strategies: Investing in tax-efficient funds or assets can help minimize the tax impact on your retirement savings.
- Plan your withdrawals strategically: By carefully planning when and how much you withdraw from your retirement accounts, you can optimize your tax situation and potentially reduce your overall tax burden.
Tax Planning for Investments
When it comes to investing, tax planning is a crucial aspect that can significantly impact your overall returns. By understanding the tax implications of different types of investments, you can make strategic decisions to minimize your tax burden and maximize your profits.
Tax Considerations when Investing
- Stocks: When investing in stocks, you may be subject to capital gains tax on any profits you make when selling shares. It’s important to consider the holding period of your investments, as short-term capital gains are typically taxed at a higher rate than long-term capital gains.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments can offer various tax benefits, such as deductions for mortgage interest, property taxes, and depreciation. Additionally, capital gains from the sale of real estate are also subject to tax, so it’s essential to plan accordingly.
- Other Assets: Different types of assets, such as bonds, mutual funds, and alternative investments, may have unique tax implications that you need to consider when planning your investment strategy.
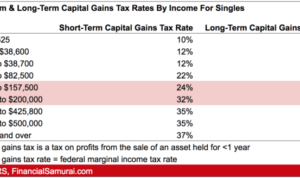
Short-term vs. Long-term Capital Gains
- Short-term capital gains are typically taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be significantly higher than the tax rate for long-term capital gains.
- Long-term capital gains, on the other hand, are subject to lower tax rates, providing an incentive for investors to hold onto their investments for an extended period.
Tips for Strategic Investment Planning
- Diversify your portfolio to spread risk and potentially reduce tax liabilities.
- Consider tax-efficient investment strategies, such as investing in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s.
- Take advantage of tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains with capital losses, reducing your overall tax bill.