Diving into the world of investment vehicles, buckle up as we explore the ins and outs of different options available to savvy investors. From stocks to real estate, we’ll break down the key differences and help you navigate the complex landscape of investment opportunities.
Whether you’re a risk-taker or prefer a more conservative approach, understanding the various characteristics of investment vehicles is crucial to making informed financial decisions. So, let’s roll up our sleeves and dig into the world of investing!
Types of Investment Vehicles
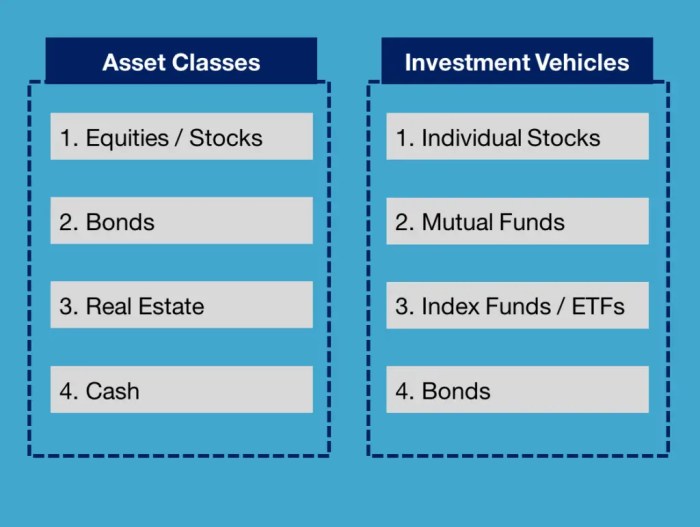
Investment vehicles are various options that investors can use to grow their money over time. These vehicles can range from traditional assets like stocks and bonds to alternative investments like real estate and commodities.
Traditional Investment Vehicles
Traditional investment vehicles are assets that have been around for a long time and are commonly used by investors. They include:
- Stocks: Shares of ownership in a company that can be bought and sold on the stock market.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by corporations or governments that pay interest over time.
- Mutual Funds: Pooled funds from multiple investors used to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities.
Alternative Investment Vehicles
Alternative investment vehicles offer investors a way to diversify their portfolios beyond stocks and bonds. Some popular examples include:
- Real Estate: Investing in properties like residential homes, commercial buildings, or land.
- Commodities: Investing in physical goods like gold, oil, or agricultural products.
- Hedge Funds: Private investment funds that use various strategies to generate returns for investors.
Risk and Return Characteristics
Investing in different vehicles comes with varying levels of risk and potential returns. Understanding these characteristics is crucial in making informed investment decisions.
Variability in Risk and Return Profiles
- Low-risk, low-return investments such as savings accounts or certificates of deposit offer minimal risk of loss but also provide lower potential returns compared to other investment options.
- High-risk, high-return investments like individual stocks or cryptocurrency have the potential for significant returns but also come with a higher risk of loss due to market volatility.
Impact of Risk Tolerance on Investment Choices
Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s willingness and ability to endure fluctuations in the value of their investments. It plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable investment vehicles for an investor.
- Investors with low risk tolerance may opt for safer investment options like bonds or index funds to minimize potential losses.
- On the other hand, investors with a higher risk tolerance may choose to allocate a portion of their portfolio to more aggressive investments like growth stocks or real estate.
Liquidity and Investment Horizon
When it comes to investing, understanding liquidity and investment horizon is crucial for making informed decisions. Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset can be bought or sold in the market without significantly affecting its price. Investment horizon, on the other hand, is the length of time an investor plans to hold an investment before selling it.
Liquidity of Different Investment Vehicles
- Stocks: Stocks are considered highly liquid as they can be easily bought and sold on the stock exchange. Investors can quickly convert their stocks into cash.
- Bonds: Bonds are generally less liquid compared to stocks. While they can still be sold, the process may take longer, especially for less popular or lower-rated bonds.
- Real Estate: Real estate is considered relatively illiquid as it can take time to sell a property and convert it into cash. The real estate market can also be influenced by various factors, impacting the speed of transactions.
Investment Horizon and Choice of Investment Vehicles
- Short-term Investment Horizon: For investors with a short-term investment horizon, liquidity becomes crucial. They may prefer more liquid assets like stocks that can be easily bought and sold to take advantage of market fluctuations.
- Long-term Investment Horizon: Investors with a long-term horizon may be less concerned about liquidity as they are willing to hold onto investments for an extended period. They may choose less liquid assets like real estate, focusing on long-term growth and appreciation.
- Diversification: Regardless of the investment horizon, diversifying across different asset classes with varying levels of liquidity can help manage risk and optimize returns over time.
Tax Implications and Regulatory Considerations
When it comes to investing, understanding the tax implications and regulatory considerations is crucial for maximizing returns and avoiding potential pitfalls.
Explain how tax implications differ across various investment vehicles:
Tax Implications Across Investment Vehicles
- Stocks: Capital gains from selling stocks are typically taxed at a lower rate if held for more than a year.
- Bonds: Interest income from bonds is taxed as ordinary income.
- Real Estate: Rental income from real estate properties is subject to taxation, but depreciation can provide tax benefits.
Discuss regulatory considerations that investors need to be aware of when choosing investment vehicles:
Regulatory Considerations for Investors
- SEC Regulations: Understanding and complying with regulations set by the Securities and Exchange Commission is crucial for protecting investments.
- Tax Laws: Keeping up with changes in tax laws can help investors optimize their tax strategies and minimize tax liabilities.
- Investment Advisor Regulations: Working with registered investment advisors who adhere to regulatory standards can provide peace of mind for investors.
Provide examples of tax-efficient investment vehicles and how they can impact overall returns:
Tax-Efficient Investment Vehicles
- ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds): ETFs are known for their tax efficiency due to their structure, which minimizes capital gains distributions.
- Index Funds: Similar to ETFs, index funds also tend to be tax-efficient because they have lower turnover rates compared to actively managed funds.
- 401(k) Plans: Contributing to a 401(k) plan can provide tax advantages such as tax-deferred growth and potential employer matching contributions.