Get ready to dive into the world of Understanding inflation rates, where we break down complex economic concepts in a way that’s fresh and engaging.
Inflation rates are more than just numbers – they impact our daily lives in ways we might not even realize.
Overview of Inflation Rates
Inflation rates refer to the percentage increase in prices of goods and services over a specific period of time. It indicates the rate at which the purchasing power of a currency is decreasing.
Impact of Inflation Rates on the Economy
Inflation rates have a significant impact on the economy as they affect various aspects such as consumer spending, investment decisions, and savings. High inflation rates can lead to a decrease in purchasing power, making it more expensive for consumers to buy goods and services. This can result in a decrease in overall economic activity and lower standards of living for the population.
- High inflation rates can erode the value of savings and fixed incomes, causing financial insecurity for individuals.
- Businesses may struggle to plan for the future due to uncertain price levels, impacting investment decisions and economic growth.
- Central banks often aim to maintain a stable inflation rate to promote economic stability and growth.
Calculation of Inflation Rates
Inflation rates are typically calculated using the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Producer Price Index (PPI). The CPI measures changes in the prices of a basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households, while the PPI tracks changes in the prices received by producers.
Formula for Inflation Rate: ((Current CPI – Previous CPI) / Previous CPI) x 100
- To calculate the inflation rate, the percentage change in the index from one period to another is determined.
- This calculation helps economists and policymakers assess the overall price level in the economy and make informed decisions.
- Understanding inflation rates is crucial for managing economic policies and ensuring stability in the financial system.
Types of Inflation
Inflation can take different forms, each impacting consumers and businesses in unique ways.
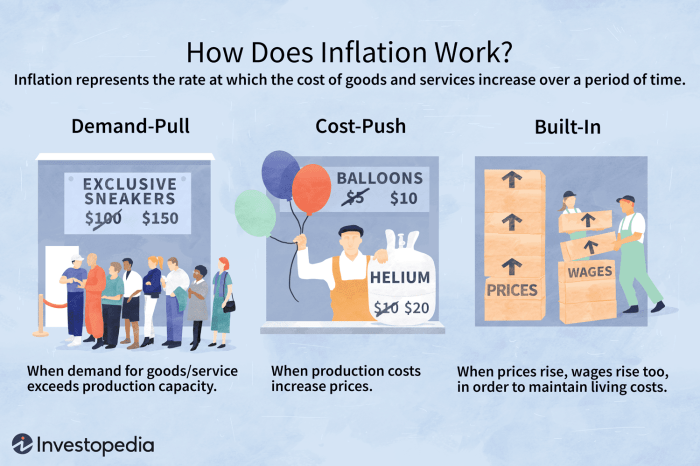
Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds supply, leading to an increase in prices. Consumers may experience higher costs for everyday items, reducing their purchasing power. On the other hand, businesses may benefit from increased revenue due to higher prices for their products or services. A real-world example of demand-pull inflation is when an unexpected surge in consumer demand causes prices to rise rapidly.
Cost-Push Inflation
Cost-push inflation happens when the cost of production increases, leading to higher prices for consumers. This type of inflation can be detrimental to both consumers and businesses. Consumers may face rising prices without a corresponding increase in income, reducing their standard of living. Meanwhile, businesses may struggle to maintain profit margins as production costs rise. An example of cost-push inflation is when an increase in raw material prices causes the overall cost of production to go up.
Built-In Inflation
Built-in inflation is a result of past inflation influencing current price levels. This type of inflation is often linked to wage-price spirals, where rising wages lead to higher prices, which in turn lead to demands for higher wages. Consumers may find themselves in a cycle of increasing costs and decreasing purchasing power. Businesses may struggle to keep up with rising labor costs and may need to increase prices to maintain profitability. A real-world example of built-in inflation is when annual wage increases lead to a continuous rise in prices across the economy.
Factors Influencing Inflation Rates
Inflation rates are influenced by a variety of factors that can impact the overall economy. Understanding these key factors is essential in analyzing the trends and fluctuations in inflation rates.
Government Policies Impact
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping inflation rates. Fiscal policies, such as tax rates and government spending, can either stimulate or slow down the economy, leading to changes in inflation rates. Additionally, monetary policies set by central banks, like interest rates and money supply, also impact inflation rates significantly.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The basic economic principle of supply and demand directly affects inflation rates. When demand for goods and services surpasses supply, prices tend to rise, leading to inflation. On the other hand, when supply exceeds demand, prices may fall, causing deflation. Understanding these dynamics is key in predicting inflation trends.
International Trade Influence
International trade plays a vital role in influencing inflation rates. The exchange rate of a country’s currency, trade agreements, and import/export policies can all impact inflation. Changes in global economic conditions and trade relationships can lead to fluctuations in inflation rates within a country.
Relationship Between Interest Rates and Inflation
Interest rates and inflation are closely linked. Central banks often adjust interest rates to control inflation. When interest rates are raised, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to lower consumer spending and decreased demand, which can help curb inflation. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate borrowing and spending, potentially leading to higher inflation rates.
Effects of Inflation Rates
When it comes to inflation rates, the impact on the economy and individuals can be significant. Let’s dive into how high and low inflation rates affect various aspects of our financial lives.
Impact on Purchasing Power
High inflation rates can erode the purchasing power of consumers, meaning that the same amount of money buys fewer goods and services. This can lead to a decrease in the standard of living for individuals as prices rise faster than wages. On the other hand, low inflation rates can signal economic stability and make it easier for consumers to plan and budget for their expenses.
Effects on Savings, Investments, and Borrowing
Inflation rates also have a direct impact on savings, investments, and borrowing. High inflation rates can devalue savings over time, making it harder for individuals to achieve their financial goals. Investors may seek assets that can outpace inflation, while borrowers may benefit from fixed-rate loans as the real value of their debt decreases with inflation. Conversely, low inflation rates can provide a more stable environment for savings, investments, and borrowing.
Historical Consequences of Inflation Rates
Throughout history, there have been several instances where inflation rates have had significant consequences. One notable example is the hyperinflation in Germany during the Weimar Republic in the 1920s, where prices skyrocketed, leading to economic chaos and social unrest. Another example is the stagflation of the 1970s, where high inflation coupled with high unemployment posed challenges for policymakers in combating both issues simultaneously.
Managing Inflation
Managing inflation is crucial for maintaining a stable economy and ensuring the purchasing power of a currency. Central banks employ various strategies to control inflation, with monetary policy playing a significant role in this process. Individuals can also take steps to protect their finances during periods of high inflation.
Strategies Used by Central Banks
- Central banks adjust interest rates: By raising interest rates, central banks aim to decrease consumer spending and borrowing, which can help reduce inflation.
- Open market operations: Central banks buy or sell government securities to influence the money supply, impacting inflation rates.
- Reserve requirements: Central banks can adjust the amount of reserves banks are required to hold, affecting the lending capacity and money supply in the economy.
Role of Monetary Policy
- Monetary policy involves controlling the money supply and interest rates to influence inflation rates. By adjusting these factors, central banks can help stabilize prices and prevent rapid inflation.
- Through monetary policy, central banks aim to strike a balance between promoting economic growth and keeping inflation in check.
Protecting Finances During High Inflation
- Invest in assets that appreciate in value: During inflationary periods, investing in assets like real estate, precious metals, or stocks can help protect the value of your money.
- Consider inflation-protected securities: Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) offer protection against inflation by adjusting their principal value based on changes in the Consumer Price Index.
- Review and adjust your budget: In times of high inflation, it’s essential to reevaluate your budget, cut unnecessary expenses, and focus on essential purchases to mitigate the impact of rising prices.